FastNetMon 也可以结合 BGP 协议,打造自动化的抗 DDoS 安全防御系统。当发现受到攻击的时候,通过在 BGP 上宣告 blocked 受到攻击的 IP 地址。从而将攻击转移到其他地点,保证本地的其他服务不受到 DDoS 攻击的影响。
测试环境:Centos7
- 安装 FastNetMon
官网:https://fastnetmon.com/install/
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pavel-odintsov/fastnetmon/master/src/fastnetmon_install.pl -Ofastnetmon_install.pl
sudo perl fastnetmon_install.pl --do-not-track-me- 使用 pf_ring 作为 FastNetMon 的抓包引擎
FastNetMon 在安装的时候,已经安装了 pf_ring 。
如果有比较新的发行版(内核 >= 3.6)可以开启 AF_PACKET ,安装并启动 irqbalance 来获得更好的抓包性能。
首先编辑文件 /etc/fastnetmon.conf,将 mirror 的值改为 on ,这将使用 pf_ring 作为抓包引擎。
# PF_RING traffic capture, enough fast but wire speed version need paid license
mirror = on同时,可以顺便把报警阈值调小一点,方便后面测试攻击。
# Limits for Dos/DDoS attacks threshold_pps = 200
threshold_mbps = 10
threshold_flows = 350编辑 /etc/networks_list 以CIDR格式添加需要监控的网段。
保存启动并保持在后台运行,同时可以添加到 /etc/rc.d/rc.local 开机启动。
/opt/fastnetmon/fastnetmon --daemonize查看日志
tail -f /var/log/fastnetmon.log- 模拟 DDoS 攻击测试 FastNetMon
接下来我们测试 fastnetmon 是否能正确识别 DDoS 攻击。
首先我们配置一下 FastNetMon 的通知脚本
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pavel-odintsov/fastnetmon/master/src/notify_about_attack.sh -O/usr/local/bin/notify_about_attack.sh
chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/notify_about_attack.sh编辑这个脚本,找到 ban 的条件语句,由于只是进行测试,我仅仅输出一条消息到 /var/log/ban.log 日志中。
if [ "$4" = "ban" ]; then
echo "FastNetMon Guard: IP $1 blocked because $2 attack with power $3 pps" >> /var/log/ban.log
exit 0
fi这样通知脚本就配置好了。
我使用 iperf 工具来模拟 DDoS 攻击,这个工具一般用于测试网络带宽,当然也可以通过大量发包模拟一次 DDoS 攻击。
在 CentOS 上可以通过 yum 直接安装 iperf:yum install iperf。
然后通过iperf -su命令启动 iperf 的服务器端。
这里 -u 参数指明侦听 udp 端口。
我将我的 mbp 作为攻击的发器端,同样安装 iperf : brew install iperf。
在客户端上向服务器发起探测:iperf -u -c 10.1.2.137 -b 100M -P 5。
这时,在服务器上执行 FastNetMon 的客户端命令 /opt/fastnetmon/fastnetmon_clinet 进行查看,可以看到出现如下信息。
FastNetMon v1.0 FastVPS Eesti OU (c) VPS and dedicated: http://FastVPS.host
IPs ordered by: packets
Incoming traffic 42594 pps 491 mbps 0 flows
10.1.2.137 35552 pps 410 mbps 0 flows *banned*
Outgoing traffic 1 pps 0 mbps 0 flows
10.1.2.137 1 pps 0 mbps 0 flows *banned*
Internal traffic 0 pps 0 mbps
Other traffic 0 pps 0 mbps
Screen updated in: 0 sec 191 microseconds
Traffic calculated in: 0 sec 7 microseconds
Total amount of not processed packets: 0
Packets received: 404792
Packets dropped: 0
Packets dropped: 0.0 %
Ban list:
10.1.2.137/35552 pps incoming at 04_06_16_00:40:13因为之前我设置了攻击阈值为 200 pps,10 mb,目前的这个负载量已经远远超过我设定的阈值,被认为遭到了攻击。可以看到,目前 10.1.2.137 这个 IP 已经被拉进 Ban list 之中了。
现在我们查看 FastNetMon 是否触发了通知,查看 /var/log/ban.log 这个日志,可以看到通知的消息。
FastNetMon Guard: IP 10.1.2.137 blocked because incoming attack with power 293 ppsFastNetMon 确实触发了通知的操作。
- FastNetMon 集成 InfluxDB
官网:https://portal.influxdata.com/downloads/
安装InfluxDB
wget https://dl.influxdata.com/influxdb/releases/influxdb-1.7.6.x86_64.rpm
sudo yum localinstall influxdb-1.7.6.x86_64.rpm编辑 InfluxDB 的配置文件 /etc/influxdb/influxdb.conf 中的 graphite 选项,按照如下配置:
[[graphite]]
enabled = true
bind-address = "127.0.0.1:2003"
database = "dc1"
protocol = "tcp"
consistency-level = "one"
name-separator = "."
# batch-size / batch-timeout requires InfluxDB >= 0.9.3
batch-size = 5000 # will flush if this many points get buffered
batch-timeout = "1s" # will flush at least this often even if we haven't hit buffer limit
templates = [
"fastnetmon.hosts.* app.measurement.cidr.direction.function.resource",
"fastnetmon.networks.* app.measurement.cidr.direction.resource",
"fastnetmon.total.* app.measurement.direction.resource"
]现在就可以启动 InfluxDB 了。
systemctl start influxdb 同样,需要在 FastNetMon 的配置文件 /etc/fastnetmon.conf 里做一些配置。
graphite = on
graphite_host = 127.0.0.1
graphite_port = 2003
graphite_prefix = fastnetmon保存好后重启FastNetMon。
- 安装配置 Grafana
官网:https://grafana.com/grafana/download
安装Grafana
wget https://dl.grafana.com/oss/release/grafana-6.1.6-1.x86_64.rpm
sudo yum localinstall grafana-6.1.6-1.x86_64.rpm启动。
service grafana-server startInfluxDB作为数据源添加,并通过Grafana官方给出示例模板添加图表。
模板链接:https://grafana.com/dashboards/7378
如果正确配置,这时已经可以看到数据了。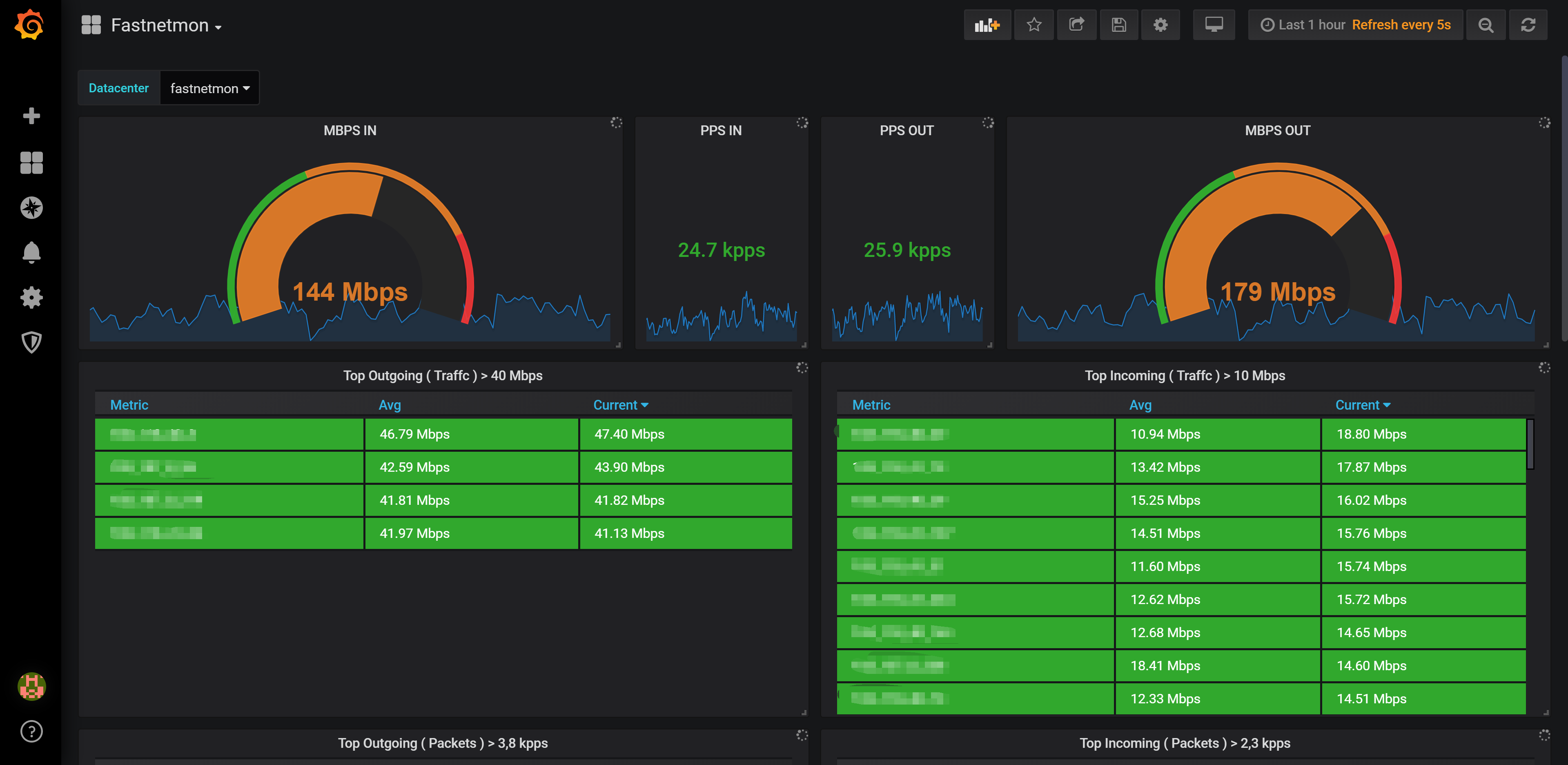
附Fastnetmon配置文件:
###
### Main configuration params
###
### Logging configuration
# enable this option if you want to send logs to local syslog facility
logging:local_syslog_logging = off
# enable this option if you want to send logs to a remote syslog server via UDP
logging:remote_syslog_logging = off
# specify a custom server and port for remote logging
logging:remote_syslog_server = 10.10.10.10
logging:remote_syslog_port = 514
# Enable/Disable any actions in case of attack
enable_ban = on
# disable processing for certain direction of traffic
process_incoming_traffic = on
process_outgoing_traffic = on
# How many packets will be collected from attack traffic
ban_details_records_count = 500
# How long (in seconds) we should keep an IP in blocked state
# If you set 0 here it completely disables unban capability
ban_time = 1900
# Check if the attack is still active, before triggering an unban callback with this option
# If the attack is still active, check each run of the unban watchdog
unban_only_if_attack_finished = on
# enable per subnet speed meters
# For each subnet, list track speed in bps and pps for both directions
enable_subnet_counters = on
# list of all your networks in CIDR format
networks_list_path = /etc/networks_list
# list networks in CIDR format which will be not monitored for attacks
white_list_path = /etc/networks_whitelist
# redraw period for client's screen
check_period = 1
# Connection tracking is very useful for attack detection because it provides huge amounts of information,
# but it's very CPU intensive and not recommended in big networks
enable_connection_tracking = off
# Different approaches to attack detection
ban_for_pps = on
ban_for_bandwidth = on
ban_for_flows = off
# Limits for Dos/DDoS attacks
threshold_pps = 20000
threshold_mbps = 1000
threshold_flows = 3500
# Per protocol attack thresholds
# We don't implement per protocol flow limits, sorry :(
# These limits should be smaller than global pps/mbps limits
threshold_tcp_mbps = 100000
threshold_udp_mbps = 100000
threshold_icmp_mbps = 100000
threshold_tcp_pps = 100000
threshold_udp_pps = 100000
threshold_icmp_pps = 100000
ban_for_tcp_bandwidth = off
ban_for_udp_bandwidth = off
ban_for_icmp_bandwidth = off
ban_for_tcp_pps = off
ban_for_udp_pps = off
ban_for_icmp_pps = off
###
### Traffic capture methods
###
# PF_RING traffic capture, fast enough but the wirespeed version needs a paid license
mirror = off
# Port mirroring sample rate
pfring_sampling_ratio = 1
# Netmap traffic capture (very fast but needs patched drivers)
mirror_netmap = off
# SnabbSwitch traffic capture
mirror_snabbswitch = off
# AF_PACKET capture engine
# Please use it only with modern Linux kernels (3.6 and more)
# And please install birq for irq ditribution over cores
mirror_afpacket = off
# use PCI-e addresses here instead of OS device names. You can find them in "lspci" output
interfaces = eth0
# Port mirroring sampling ratio
netmap_sampling_ratio = 1
# This option should be enabled if you are using Juniper with mirroring of the first X bytes of packet: maximum-packet-length 110;
netmap_read_packet_length_from_ip_header = off
# Pcap mode, very slow and thus not suitable for production
pcap = off
# Netflow capture method with v5, v9 and IPFIX support
netflow = on
# sFLOW capture suitable for switches
sflow = off
# PF_RING configuration
# If you have a license for PF_RING ZC, enable this mode and it might achieve wire speed for 10GE
enable_pf_ring_zc_mode = off
# Configuration for netmap, mirror, pcap modes
# For pcap and PF_RING we could specify "any"
# For netmap and PF_RING we could specify multiple interfaces = eth0
interfaces = eth0
# We use average values for traffic speed to certain IP and we calculate average over this time slice
average_calculation_time = 5
# We use average values for traffic speed for subnet and we calculate average over this time slice
average_calculation_time_for_subnets = 20
# Netflow configuration
# it's possible to specify multiple ports here, using commas as delimiter
netflow_port = 1234
netflow_host = 0.0.0.0
# To bind to all interfaces = eth0
# To bind to all interfaces = eth0
# To bind to localhost for a specific protocol: ::1 or 127.0.0.1
# Netflow v9 and IPFIX agents use different and very complex approaches for notifying about sample ratio
# Here you could specify a sampling ratio for all this agents
# For NetFLOW v5 we extract sampling ratio from packets directely and this option not used
netflow_sampling_ratio = 1
# In some cases with NetFlow we could get huge bursts related to aggregated data nature
# We could try to get smoother data with this option, i.e. we will divide counters on collection interval time
netflow_divide_counters_on_interval_length = off
# Process each netflow packet with LUA
# This option is not default and you need build it additionally
# netflow_lua_hooks_path = /usr/src/fastnetmon/src/netflow_hooks.lua
# sFLOW configuration
# It's possible to specify multiple ports here, using commas as delimiter
sflow_port = 6343
# sflow_port = 6343,6344
sflow_host = 0.0.0.0
# process each sFLOW packet with LUA
# This option is not default and you need build it additionally
# sflow_lua_hooks_path = /usr/src/fastnetmon/src/sflow_hooks.lua
# sFlow processing QinQ
sflow_qinq_process = off
# sFlow ethertype of outer tag in QinQ
sflow_qinq_ethertype = 0x8100
###
### Actions when attack detected
###
# This script executed for ban, unban and attack detail collection
notify_script_path = /usr/local/bin/notify_about_attack.sh
# pass attack details to notify_script via stdin
# Pass details only in case of "ban" call
# No details will be passed for "unban" call
notify_script_pass_details = on
# collect a full dump of the attack with full payload in pcap compatible format
collect_attack_pcap_dumps = off
# Execute Deep Packet Inspection on captured PCAP packets
process_pcap_attack_dumps_with_dpi = off
# Save attack details to Redis
redis_enabled = off
# Redis configuration
redis_port = 6379
redis_host = 127.0.0.1
# specify a custom prefix here
redis_prefix = mydc1
# We could store attack information to MongoDB
mongodb_enabled = off
mongodb_host = localhost
mongodb_port = 27017
mongodb_database_name = fastnetmon
# If you are using PF_RING non ZC version you could block traffic on host with hardware filters
# Please be aware! We can not remove blocks with this action plugin
pfring_hardware_filters_enabled = off
# announce blocked IPs with BGP protocol with ExaBGP
exabgp = off
exabgp_command_pipe = /var/run/exabgp.cmd
exabgp_community = 65001:666
# specify multiple communities with this syntax:
# exabgp_community = [65001:666 65001:777]
# specify different communities for host and subnet announces
# exabgp_community_subnet = 65001:667
# exabgp_community_host = 65001:668
exabgp_next_hop = 10.0.3.114
# In complex cases you could have both options enabled and announce host and subnet simultaneously
# Announce /32 host itself with BGP
exabgp_announce_host = on
# Announce origin subnet of IP address instead IP itself
exabgp_announce_whole_subnet = off
# Announce Flow Spec rules when we could detect certain attack type
# Please we aware! Flow Spec announce triggered when we collect some details about attack,
# i.e. when we call attack_details script
# Please disable exabgp_announce_host and exabgp_announce_whole_subnet if you want to use this feature
# Please use ExaBGP v4 only (Git version), for more details: https://github.com/pavel-odintsov/fastnetmon/blob/master/docs/BGP_FLOW_SPEC.md
exabgp_flow_spec_announces = off
# GoBGP intergation
gobgp = off
gobgp_next_hop = 0.0.0.0
gobgp_announce_host = on
gobgp_announce_whole_subnet = off
# Graphite monitoring
# InfluxDB is also supported, please check our reference:
# https://github.com/pavel-odintsov/fastnetmon/blob/master/docs/INFLUXDB_INTEGRATION.md
graphite = on
# Please use only IP because domain names are not allowed here
graphite_host = 127.0.0.1
graphite_port = 2003
# Default namespace for Graphite data
graphite_prefix = fastnetmon
# Add local IP addresses and aliases to monitoring list
# Works only for Linux
monitor_local_ip_addresses = on
# Create group of hosts with non-standard thresholds
# You should create this group before (in configuration file) specifying any limits
hostgroup = my_hosts:10.10.10.221/32,10.10.10.222/32
# Configure this group
my_hosts_enable_ban = off
my_hosts_ban_for_pps = off
my_hosts_ban_for_bandwidth = off
my_hosts_ban_for_flows = off
my_hosts_threshold_pps = 20000
my_hosts_threshold_mbps = 1000
my_hosts_threshold_flows = 3500
# Path to pid file for checking "if another copy of tool is running", it's useful when you run multiple instances of tool
pid_path = /var/run/fastnetmon.pid
# Path to file where we store information for fastnetmon_client
cli_stats_file_path = /tmp/fastnetmon.dat
# Enable gRPC api (required for fastnetmon_api_client tool)
enable_api = off
###
### Client configuration
###
# Field used for sorting in client, valid values are: packets, bytes or flows
sort_parameter = packets
# How much IPs will be listed for incoming and outgoing channel eaters
max_ips_in_list = 7参考文章:
http://echohn.github.io/2016/06/03/use-fastnetmon-and-grafana-to-build-a-graphical-ddos-early-warning-system/
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41004350/article/details/78492397
http://ju.outofmemory.cn/entry/316687

学习了。